Welcome to JCS Medical Diagnostics
We are a team of medical laboratory scientists,pharmacists,doctors,nurses,biochemists,community healthcare
workers,PPmvs etc.,working together to increase Nigerian's life span from 54 years to 85 years atleast
comprehensive diagnosis,timely results and referral to the appropriate health institution as the case may be
,healthcare awareness and publications. These are our primary assignments i.e to protect life and health and
respect autonomy with fairness and justice by making sure right samples are collected,analyzed/or referred
and results obtained at the right time.
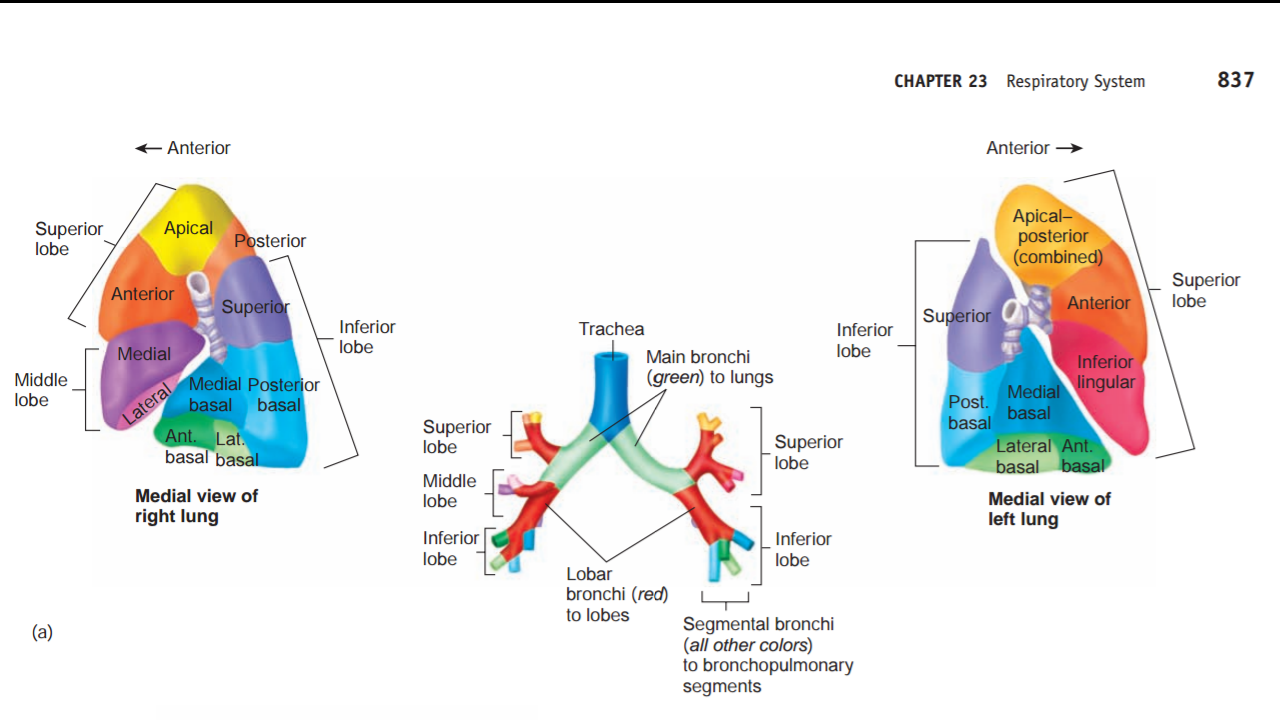
War Against Pneumoniae
H. pylori, or Helicobacter pylori, is a gram-negative, micro-aerophilic bacterium that lives
primarily in the digestive tract. It is associated with Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract,
gastric ulcers, cancers of the stomach and other stomach problems. Helicobacter pylori
symptoms include nausea, vomiting blood, and an overall loss of appetite in addition to severe
abdominal pain. Direct mouth-to-mouth transmission is the most common route of transmission,
but contaminated food or water can also spread the disease. Helicobacter pylori (H. Pylori)
infections can lead to a variety of unpleasant side effects, including gastric ulcers, gastritis, and
even stomach cancer.Open a PDF file open a .
Polymerase Chain Reactions

Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used in
molecular biology to make many copies of a specific DNA
segment. Using PCR, copies of DNA sequences are exponentially
amplified to generate thousands to millions of more copies of
that particular DNA segment. PCR is now a common and often
indispensable technique used in medical laboratory and clinical
laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including
biomedical research and criminal forensics. PCR was developed
by Kary Mullis in 1983 while he was an employee of the Cetus
Corporation. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in
1993 (along with Michael Smith) for his work in developing the
method.
...Open a PDF file open a .
DANGERS IN CONTRACEPTIVES

Contraceptive pills are pills that prevents or tends to prevent conception.
Studies indicate that contraceptives pills are effective when taken within 24
hours and before 72hours after unprotected sex or else the pills would
become useless. We have two types of contraception pills which is namely:
the combined oral contraceptive pills and the mini pill.
...Open a PDF file open a .